
PHERAstar FSX
Powerful and most sensitive HTS plate reader
Histone deacetylases or HDACs are epigenetic enzymes that remove acetyl groups from lysine residues. Find out how microplate readers can be used to measure their activity and assist drug discovery.
 Dr Barry Whyte
Dr Barry Whyte
The discovery of an enzyme that removes acetyl groups from histone dates to 1969 when Inoue and Fujimoto discovered histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity in calf thymus extract.1 This finding, which arose from curiosity-driven research, opened new areas of enquiry, led to a better understanding of epigenetics, and launched a host of clinical investigations for new drugs to treat cancer, inflammation, and neurological diseases. The first regulatory approval by the FDA for a HDAC inhibitor was in 2006 for Vorinostat – a cancer treatment for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (fig. 1). Several other drugs that target HDACs are already on the market, and more are anticipated.2,3
In this blog article, we look at the different types of HDACs and discuss ways to study them using microplate readers.
Histone deacetylase is an epigenetic effector since it removes acetyl groups (marks) from lysine residues on histones. Epigenetic changes alter the regulation of gene activity and gene expression in ways that are not dependent on the sequence of genes. Instead, epigenetic alterations arise from chemical modification of genes or proteins that affect how genes are read. Epigenetic mechanisms, which also include DNA methylation or may involve microRNAs, can therefore produce heritable phenotypic changes without a change in DNA sequence.
Histone acetylation is controlled by the opposing activities of two enzymes: histone acetyltransferase and histone deacetylase. In the “language” of epigenetics, histone acetyl transferase is a “writer” and histone deacetylase an “eraser”. Histone deacetylase activity leads to a compact chromatin structure which makes access by RNA polymerase more difficult, and thus decreases gene expression. In addition to making chromatin more condensed and making it more difficult for the transcriptional machinery to access the DNA, HDACs can also directly interact with transcription factors and modulate their activity. The interplay of writer (histone acetylation) and eraser (histone deacetylation) impacts the activities of transcription factors, transcriptional repressors, transcriptional co-repressors, and gene expression.
Overall, the removal of acetyl groups has profound effects on gene expression. Global gene expression profiling experiments estimate that the transcription of 10% of genes are regulated by histone deacetylases. However, it is uncertain how each HDAC uniquely regulates a specific set of genes, and this requires further investigation.4
In the context of the cell cycle, HDACs can regulate the expression of key genes involved in controlling cell division and differentiation. For example, HDACs can repress the expression of genes that promote cell cycle progression, which allows cells to coordinate the different stages of the cell cycle. HDACs also interact with other cellular proteins and signaling pathways that control the cell cycle. One example is the interaction with cyclin-dependent kinases.
The control of cell cycle progression, cell survival and differentiation are among the most important roles of HDAC enzymes. In the context of cancer, HDACs reverse chromatin acetylation making it harder for transcription factors to bind to DNA and thus altering the transcription of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.
Today, we know that there are at least 18 histone deacetylase proteins which fall into four classes based on their amino acid sequence homology to four yeast enzymes.2 The class I HDACs, the Rpd3-like proteins, include HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3 and HDAC8. The class II Hda1-like proteins include HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC6, HDAC7, HDAC9 and HDAC10; the class III Sir2-like proteins include SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT3, SIRT4, SIRT5, SIRT6 and SIRT7. Class IV comprises one protein: HDAC11.
The Class I, II and IV HDACs are numbered according to the chronological order of discovery.
Class I HDACs and class II histone deacetylases play a major role in the deacetylation of lysine residues in N-terminal histone tails. The classical histone deacetylase family of enzymes (Classes I, II and IV) exhibit a common catalytic mechanism that requires a Zn2+ ion. Class III histone deacetylases require NAD+ as a cofactor for enzyme activity.
The class I HDACs, which include the zinc-dependent HDACs 1, 2, 3 and 8, consist of 350-500 amino acid residues. The class II HDACs are also zinc dependent but are larger and consist of around 1000 amino acid residues. The class I HDACs and class II HDACs can be inhibited by trichostatin A and this inhibitor is often used as a reference to benchmark these enzymes. The class III HDACs are NAD-dependent sirtuin enzymes. HDAC11, the sole member of class IV, regulates the protein stability of DNA replication factor CDT1 and the expression of interleukin 10. However, HDAC11 remains one of the least studied of the classical HDAC family.4
Acetylated proteins are widespread in cells. A study using mass spectroscopy looking at the human proteome identified 1750 proteins with a total of 3600 lysine acetylation sites.6 Histone deacetylases are also known to be active on non-histone proteins.
The acetylation of lysine residues also impacts the extent of phosphorylation of proteins. It is also frequently observed on proteins that are involved in the control of other proteins by ubiquitination and on proteins that form large macromolecular complexes. Acetylation of lysine residues is therefore implicated in cell biology events that extend beyond its role with histones.
The activities of histone deacetylases are highly regulated. Regulation takes place by different mechanisms at the level of transcription and transcription factors, posttranscription, translation and posttranslational levels. Protein-protein interactions and posttranslational modifications have been studied the most and are well defined. Less studied, are the regulation of some histone deacetylases by the control of gene expression, transcription factor regulation, alternative RNA splicing, availability of cofactors, subcellular localization, and proteolytic processing.
The function or expression of histone deacetylase is often affected in cancer, neurological syndromes, and immune disorders. If epigenetic regulation is perturbed, it can lead to the onset and progression of several diseases. Interest is therefore high in finding small-molecule chemical compounds that can function as histone deacetylase inhibitors.
A few decades after the discovery of HDACs, researchers determined crystal structures for several bacterial and human HDACs (fig. 1). The first X-ray crystal structure of a classical histone deacetylase family protein was determined by Finnin and coworkers for the histone deacetylase-like protein from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Aquifex aeolicus.5 These structures have helped reveal the mechanisms of action of the different class I-IV HDACs. In addition, the structural analyses provide a framework for the future design of tight-binding inhibitors for this important drug target.
HDAC inhibitors are a diverse group of small-molecule drugs that induce a broad range of effects on cancer cells, including cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, cell differentiation, autophagy and anti-angiogenic effects. The past few decades have witnessed extensive study of around 30 HDAC inhibitors in clinical trials. Most of the early studies focused on the development of new cancer treatments and were mainly applied to treat hematological malignancies. More recently, HDAC inhibitors have been shown to have potential for the treatment of metabolic diseases like diabetes, neurological diseases like multiple sclerosis, and in some cases viral infections. HDAC inhibitors are being investigated either alone or in combination with other agents for future cancer therapies. In addition, histone acetylation states have also been linked to lifespan regulation and studies are in progress to investigate opportunities to develop healthy ageing drugs.7
Histone deacetylase inhibitors have been discovered from natural sources or made synthetically. Many are being studied clinically. These inhibitors can be classified according to their chemical structures into the following groups: hydroxamic acids; cyclic peptides, short chain fatty acids, benzamides; and electrophilic ketones.
Trichostatin A, which was isolated from the culture broth of Streptomyces platensis, was one of the first HDAC inhibitors to be identified. At nanomolar concentrations it inhibits histone deacetylase activity, and this inhibition is reversible. Trichostatin A is a hydroxamic acid HDAC inhibitor and is often used to investigate histone acetylation. Vorinostat, the first histone deacetylase inhibitor to be approved by the FDA, is also a hydroxamic acid. Most HDAC inhibitors are not selective for specific histone deacetylase enzymes and the identification of selective HDAC inhibitors has proved challenging.
High-throughput screening provides an effective way to look at many targets to find new inhibitors.8 Histone deacetylases can be targeted using small molecule chemical agents. With this in mind, it is useful to have access to a wide range of biochemical assays that permit monitoring of histone deacetylase activity and allow assessment of the impact of inhibitors. When these assays are compatible with microplates, researchers have access to greater efficiencies through use of a microplate reader, saving time and valuable resources.
How can the study of histone deacetylases be carried out? In the past, researchers used radiolabeling methods or acetylated histone peptides. These types of assays often required separation by techniques like High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). However, such approaches are time consuming and not amenable to the throughput required for modern drug discovery. Over the years, quicker and more sensitive assays have been developed that rely on detection by techniques like fluorescence, fluorescence polarization, luminescence, chemiluminescence, and time-resolved FRET. Absorbance has also been used but generally provides low sensitivity and is susceptible to optical interference.
Fluorescence intensity can be readily used to measure histone deacetylase activity. This type of approach involves the use of a substrate with a fluorogenic label. Detection is performed by measuring the increase in fluorescence after appropriate excitation. Such assays are sensitive and less prone to optical interference than other methods that rely on for example detection by absorbance . They are often coupled to the activities of other enzymes in a second step to allow for measurement.
The application note “A fluorescence-based assay of the epigenetic enzyme histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)” describes how fluorescence can be used to measure histone deacetylase activity and the impact of inhibitors on histone deacetylase assays. The activity of recombinant HDAC1 was measured in a two-step enzyme assay in a BMG LABTECH reader using the fluorogenic substrate Boc-Lys(Ac)-AMAC. Histone deacetylase activity removes the acetyl group from the histone lysine residue. In a second step, the deacetylated substrate is cleaved by trypsin to release fluorogenic 7-amino-4-methyl coumarin (fig. 3) which is readily measured by the microplate reader.
A different type of approach involves the use of luminescence to monitor histone deacetylase activity. One way to do this is to make use of an aminoluciferin-labelled ε-acetylated lysine peptide substrate. In this type of enzyme-coupled assay, aminoluciferin is released from the peptide by the action of histone deacetylase which serves as a substrate for a luciferase enzyme.
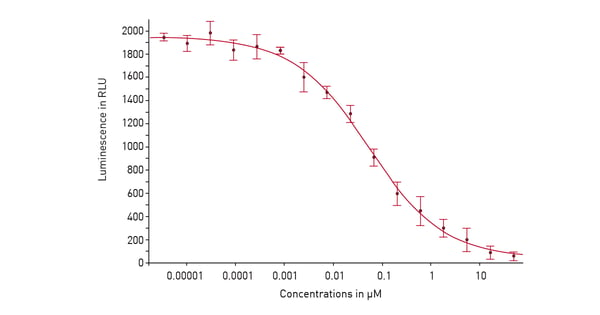
In the application note “Screening for histone deacetylase (HDAC) active compounds” a luminescence assay was used in a 384-well microplate on the PHERAstar® FSX to screen for active compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases. Detection involved using the HDAC-Glo™ I/II assay from Promega. After deacetylation of the peptide substrate, a protease was added that cleaves the deacetylated substrate. This liberates aminoluciferin which serves as a substrate for luciferase to yield a luminescent signal proportional to histone deacetylase activity (fig. 4). This is a good example of how luminescence on the PHERAstar FSX can be used for high-throughput screening assays as well as assay development at speed and scale.
Fluorescence polarization is also an option for measuring histone deacetylase activity. Competitive binding assays can make use of a fluorescently labelled ligand that binds to the histone deacetylase enzyme. When the ligand is displaced from the enzyme, there is a significant change in size and accordingly in the fluorescence polarization. This type of assay can also be used to detect compounds that displace the fluorescently labelled ligand from the histone deacetylase enzyme and can be used to determine the affinity of these compounds for the histone deacetylase enzyme.
FRET and Time-Resolved FRET are popular detection methods to measure histone deacetylase activity. Both can be used in proximity-based assays that require labelled enzymes. Each approach involves energy transfer between two introduced fluorophores that must be close together to give a signal. FRET is prone to higher background signals due to scattered excitation light and autofluorescence. TR-FRET uses longer-lived lanthanide donor fluorophores that reduce background signals and may offer advantages where high background signals are limiting with FRET. Efforts are underway to expand further the types of probes available for biological studies. CoraFluors, a new class of macrotricyclic terbium complexes, are novel fluorophores that are stable in biological media and exhibit desirable photophysical and physicochemical properties. They have found use in isoform-selective target engagement profiling of HDAC1 inhibitors in live cells.9
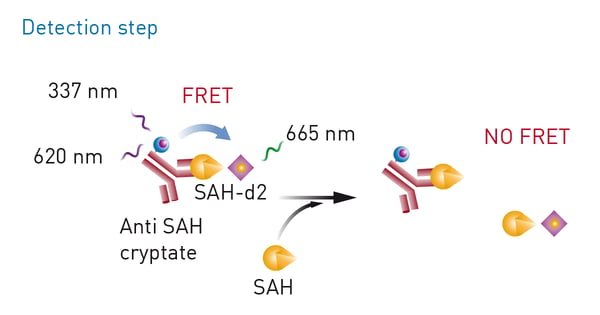
Epigenetic marks are not restricted to acetyl groups but also include other marks like methyl groups. In the application note “Miniaturization of an HTRF® methyltransferase assay that detects histone modifying activity” a Homogeneous Time Resolved Fluorescence assay was used on the PHERAstar FSX for high-throughput screening of compounds that modify the activity of methyltransferases (fig. 5). Methyltransferases are of considerable interest in drug discovery and disease research. For this assay, the EPIgeneous Methyltransferase Assay Kit from Cisbio was used. Here, detection involves measurement of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine which arises when methyltransferases act on S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Detection agents are added that contain an antibody specific to S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine and which is labelled with Lumi4-Tb cryptate. d2-coupled S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine is added which competes with S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine formed during the reaction with the antibody-binding sites. This in turn leads to a decrease in the HTRF signal.
 The assay allowed for high-throughput screening in an assay that was miniaturized tenfold leading to significant cost savings on reagents, enzymes, substrates, and compounds. Excellent data quality was achieved in a volume of 2 µl. Miniaturization of the assay was very successful as indicated by the high quality of the data. Z´ factors greater than 0.88 were achieved in an assay volume of 2 µl which agreed very well with the assay parameters obtained for the standard 20 µl assay.
The assay allowed for high-throughput screening in an assay that was miniaturized tenfold leading to significant cost savings on reagents, enzymes, substrates, and compounds. Excellent data quality was achieved in a volume of 2 µl. Miniaturization of the assay was very successful as indicated by the high quality of the data. Z´ factors greater than 0.88 were achieved in an assay volume of 2 µl which agreed very well with the assay parameters obtained for the standard 20 µl assay.
In the application note “Assessing epigenetic enzyme activity using HTRF® epigenetic assays from Cisbio with the PHERAstar® FSX from BMG LABTECH” an assay is described to detect histone methyltransferase G9a activity. This assay was used to screen for inhibitors in a 384-well format.
The assay is a histone H3K9 monomethylation assay that uses a biotinylated peptide comprised of residues 1-21 of histone H3. Lysine 9 is unmethylated and serves as a substrate for the assay. The assay is a two-step reaction comprising an enzymatic step followed by a detection step with no washing step. In the enzymatic step, the substrate, enzyme G9a, and SAM are combined. In the incubation, active enzyme results in the transfer of a methyl group to lysine resulting in methylated substrate. The modified substrate is detected by adding Eu3+ -cryptate labeled anti-H3K9me1 detection antibody and XL665-conjugated streptavidin. The antibody binds specifically to the methylated substrate and fluorescence energy transfer is observed between the HTRF donor (the antibody) and acceptor (XL665). The Cisbio HTRF® G9a Histone H3K9 Monomethylation Assay provides an excellent platform to screen for inhibitors of these enzymes that play a central role in epigenetic regulation (fig. 6).
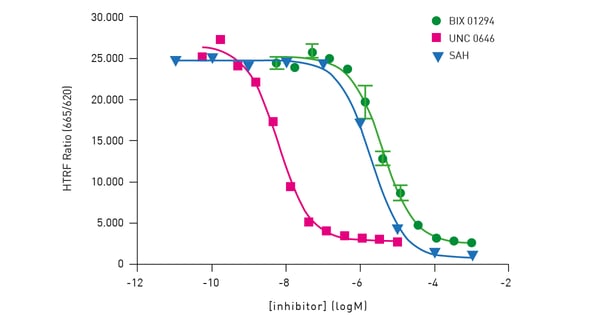 The performance of the assay on the PHERAstar FSX was verified using substrate, cofactor and inhibitor titrations. Measurements performed on the PHERAstar FSX used the laser in flying mode (1 flash) to measure the HTRF signal. The HTRF-specific modules provide simultaneous dual emission detection and excellent performance.
The performance of the assay on the PHERAstar FSX was verified using substrate, cofactor and inhibitor titrations. Measurements performed on the PHERAstar FSX used the laser in flying mode (1 flash) to measure the HTRF signal. The HTRF-specific modules provide simultaneous dual emission detection and excellent performance.
As mentioned earlier, several histone deacetylase inhibitors are currently on the market or in late-stage clinical development: Romidepsin, a natural product obtained from the bacterium Chromobacterium violaceum, is approved for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (fig. 7); Panobinostat is on the market for the treatment of multiple myeloma in combination with other therapies; Belinostat is available for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma; Valproic acid, an inhibitor of HDAC1 activity, has received regulatory approval for the treatment of seizures and bipolar disorder; Entinostat, a benzamide histone deacetylase inhibitor, is in late-stage clinical development for the treatment of various cancers.3
Today, the HDAC inhibitors that have reached the market have been effective for cancers of the blood but have proven less effective for the treatment of solid tumors. Further work is needed to come up with ways to make HDAC inhibitors more effective for the treatment of solid tumors.
In most cases, the ideal histone deacetylase inhibitor would selectively target only the specific HDAC enzyme involved in a particular disease. Further work is therefore required to improve the selectivity of HDAC inhibitors (pan-HDAC inhibitors).
Many opportunities exist to extend the use of HDAC inhibitors to new disease areas. In areas from neurodegeneration and heart disease to diabetes and sarcopenia, a wide range of age-related preclinical disease models have shown improvement upon use of HDAC inhibitors.3 In addition, epigenetics has emerged as a central target for intervention in ageing.7
While it is known that there are more than a thousand histone deacetylase substrates, the biological consequences of deacetylation of these substrates remains largely unknown.
Many acetylated non-histone proteins have been discovered in recent years and shown to be deacetylated. Further studies on the impact of HDACs on non-histone proteins will open new opportunities for the discovery of new biology and further drug development.
High-throughput screening methods with state-of-the-art molecular and cell-based assays will offer a productive avenue to finding and developing much-needed therapeutics.
What is the preferred BMG LABTECH microplate reader for specific needs and applications to measure histone deacetylases and other epigenetic targets?
The PHERAstar® FSX was specifically conceived for screening campaigns and is your go-to reader for high-performance high-throughput investigations. It is the option of choice if researchers need the highest possible sensitivity and the fastest speed at scale for histone deacetylase measurements.
Both the VANTAstar® and CLARIOstar® Plus allow for emission scanning and include Enhanced Dynamic Range technology for superior performance in a single run. They also offer increased light transmission and sensitivity courtesy of Linear Variable Filter MonochromatorsTM and different filter options.
All BMG LABTECH microplate readers have exceptionally fast reading capabilities. In addition, the Omega series, CLARIOstar Plus and PHERAstar® FSX microplate readers come with on-board injectors that can offer the very best options for detection at the time of injection.
Collectively, these multi-mode microplate readers combine high performance with miniaturized assays, short measurement times, and offer considerable savings on materials and other resources.
Powerful and most sensitive HTS plate reader
Most flexible Plate Reader for Assay Development
Upgradeable single and multi-mode microplate reader series
Flexible microplate reader with simplified workflows
Gene reporter assays are sensitive and specific tools to study the regulation of gene expression. Learn about the different options available, their uses, and the benefits of running these types of assays on microplate readers.
Life in the depths of the ocean operates under extreme conditions. Find out how proteins from deep-sea luminescent organisms are useful for measurements on microplate readers.
Next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies for DNA or RNA have made tremendous progress in recent years. Find out how microplate readers can advance the quality control of nucleic acids to facilitate NGS.
Measuring light scattering is an accurate and expedient way to determine drug solubility. Find out how the NEPHELOstar® Plus can be used for early drug solubility screening at high throughput.
Mitochondrial toxicity can have devastating effects on the cell and life. Find out how microplate readers can be used to assess mitochondrial health and how this impacts disease and drug discovery.